How Rubber Injection Molding Works
During rubber injection molding, professionals apply heat and pressure to the material to create different shapes. This method produces quality rubber parts that vehicle and aerospace industries use. Here are some steps involved in rubber molding:
Preparation of Material
In rubber molding, the first step is selecting raw rubber, which is in the form of pellets, strips, or preforms. Such materials include natural rubber, synthetic rubber, and other related materials such as Viton. Natural rubber is a tough and elastic product, which is why it is used in applications such as automotive seals and tires. Synthetic rubber may resist oil and too much friction, meaning it’s a good choice for producing gaskets and seals.
Manufacturers also select the right additives, including curing agents and accelerators that make the rubber material more resilient. After selecting materials, manufacturers weigh them according to the recipe to produce quality and consistent products. Experts use electronic scales or balances to measure the materials in grams or kilograms, depending on the batch size.
Heating and Injection
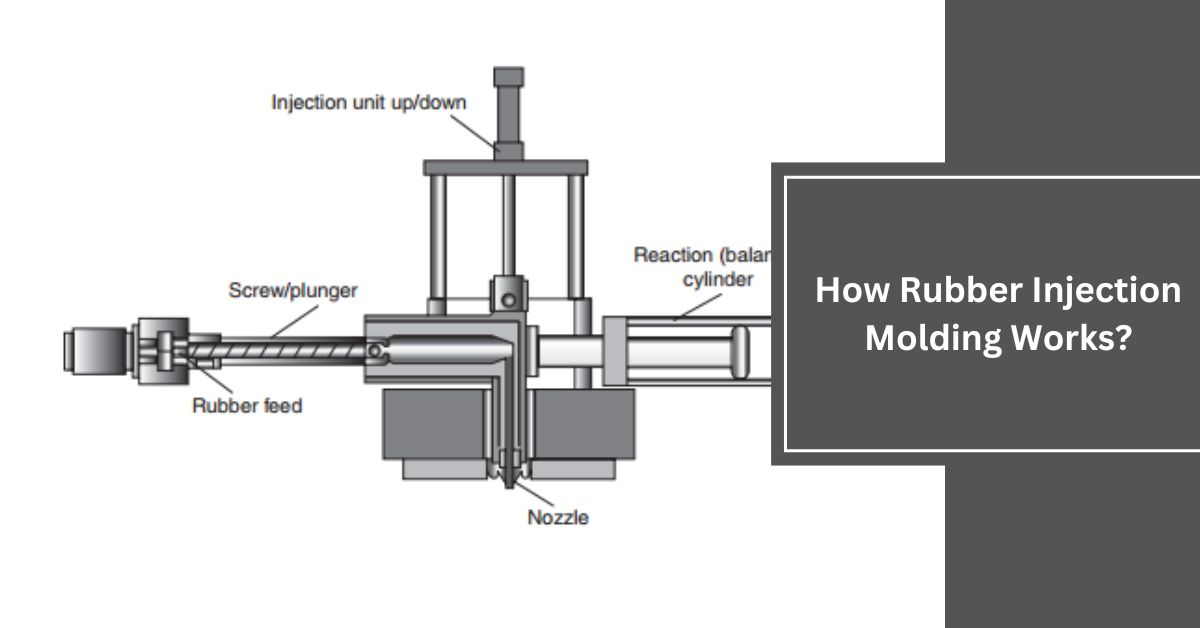
Inside the injection molding machine, workers heat the raw materials to a certain temperature. This equipment melts rubber effectively to make it soft enough for injection. By heating rubber, it can mix easily with fillers and additives, enhancing its properties.
Once the material is mixed and heated properly, experts inject it into a heated mold cavity under high pressure. This pressure allows the material to fill the mold and take its shape. Machines control the speed to prevent problems, such as air traps or incomplete filling that can affect the final result.
Curing
After filling the mold cavity with the rubber material, manufacturers close the mold and start the curing process. With the help of heat, pressure, and chemical agents, soft rubber is transformed into a strong, more durable product. Thicker rubber might need more curing time than thin rubber to make it more elastic and resistant to wear.
Heat is used for activating curing agents within the rubber compound to create long-lasting products. To attain a uniform density and minimize defects. Specialists use high pressure in the curing process. As for chemical agents, they cause the rubber molecules to form cross-links, creating a strong material.
Ejection and Finishing
Once the curing process is completed, the mold opens and manufacturers remove the newly formed rubber from the machine. Ejector pins are commonly used to remove the parts. Excess material that formed during injection is trimmed off to attain a good shape and dimension. Operators also inspect the products for problems, such as defects and incomplete curing.
For the parts to meet industry specifications, professionals add holes, slots, or intricate features. To remove minor imperfections and improve aesthetics, surfaces are polished or buffed. Some rubber parts may receive surface coatings or paint to protect them from moisture and sunlight.
Get Quality Rubber Molding Services
Trusted manufacturers use the right rubber materials and techniques to produce parts that last long and suit different industries. They also monitor the entire process to create reliable components. Call an experienced company to learn more about its rubber molding services.